Adductor Tendinopathy: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Exercises
:format(webp)/cdn.mskdoctors.com/storage/2025/3/wamnWnRQ6Qgx9SuYA29rqCNpWpIa2hql.jpg)
Key Takeaways
-
Adductor tendinopathy is characterised by pain in the groin area, especially during leg movements.
-
Common causes include overuse, muscle imbalances, and inadequate warm-ups.
-
Initial treatment involves rest, ice application, and avoiding aggravating activities.
-
Physical therapy and targeted exercises play a crucial role in recovery.
-
At MSK Doctors, we offer comprehensive musculoskeletal care, specialised treatments, and a patient-centric approach to tendon health.
What is Adductor Tendinopathy?
Definition and Overview
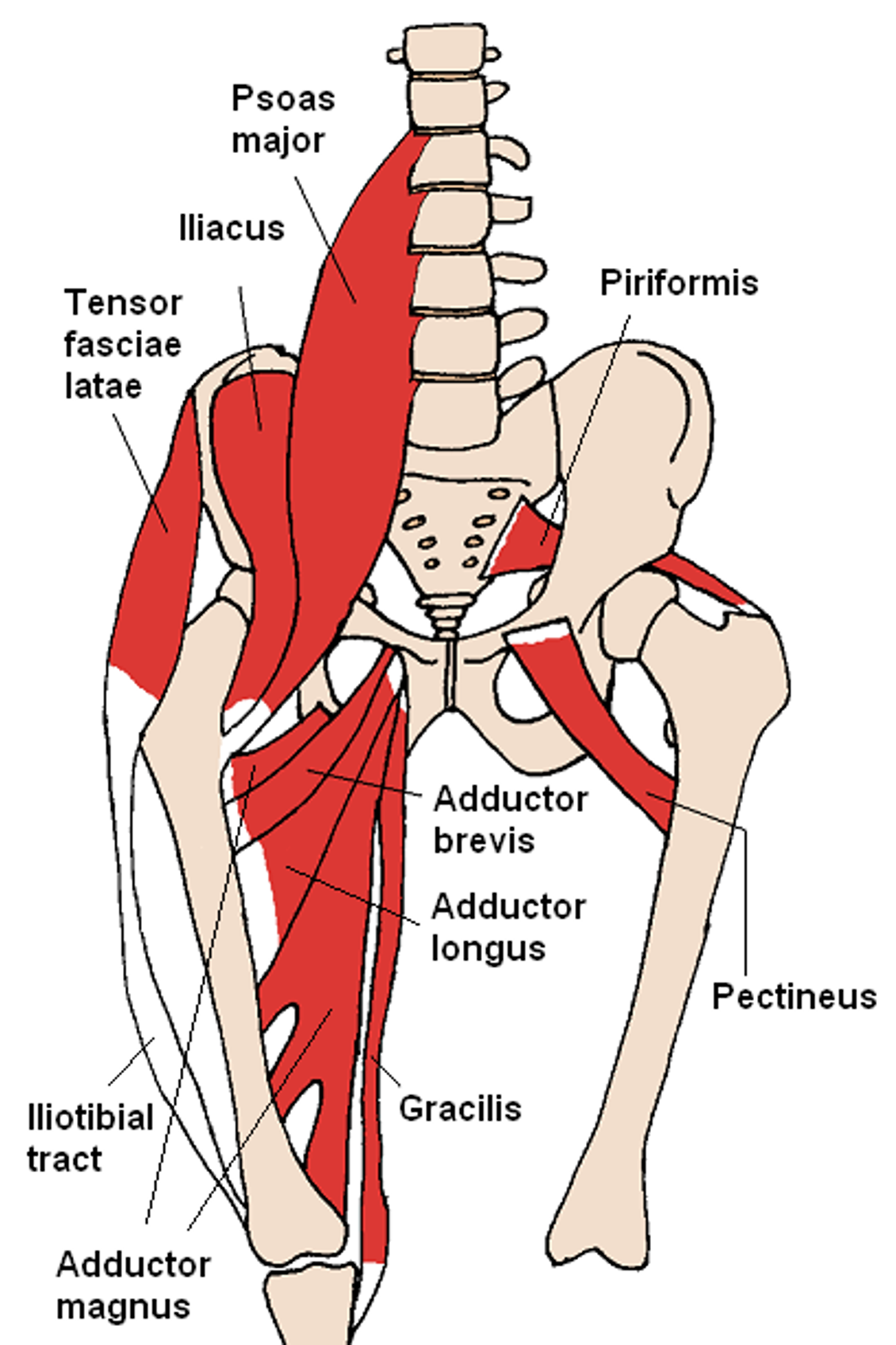
Adductor tendinopathy happens when the adductor tendons become damaged due to overuse or excessive strain. These muscles are responsible for pulling the legs together and are crucial for various movements - especially in sports (image courtesy of Wikipedia).
It's common among athletes who engage in activities involving repetitive leg movements, such as soccer, hockey, and running. But anyone can develop this condition due to muscle imbalances or improper exercise techniques.
Common Misconceptions
Some misconceptions about adductor tendinopathy that can hinder effective treatment. One common myth is that complete rest is the best solution. While rest is important, prolonged inactivity can lead to muscle weakness and delayed recovery.
Another misconception is that painkillers alone can resolve the issue. While they may provide temporary relief, addressing the underlying causes through physical therapy and exercises is crucial for long-term recovery.
|
Recognising Adductor Tendinopathy Symptoms
Typical Pain Locations
Pain is typically felt in the groin area, where the adductor muscles attach to the pelvis. This pain can radiate down the inner thigh, especially during activities that involve adduction or bringing the legs together.
For example, a soccer player may notice sharp pain when kicking a ball or changing direction quickly. Similarly, runners might experience discomfort during the push-off phase of their stride.
Movement Restrictions
Adductor tendinopathy can lead to movement restrictions. You might find it difficult to perform certain activities that involve stretching or contracting the adductor muscles.
These restrictions can affect athletic performance and everyday tasks like walking or climbing stairs.
Underlying Causes of Adductor Tendinopathy
Activities Leading to Injury
Activities that involve repetitive leg movements or sudden changes in direction can significantly stress the adductor tendons. Sports like soccer, hockey, and basketball are common causes due to their intensive nature.

Activities that require prolonged standing or awkward positions can also contribute to the development of adductor tendinopathy.
Biomechanical Contributors
Poor posture or improper movement patterns can lead to uneven distribution of stress across the adductor tendons. This imbalance may cause excessive strain on certain parts of the tendon - leading to micro-tears and inflammation.
If you tend to favor one leg over the other during activities - this can lead to overuse of the adductor muscles on that side. Improper footwear or uneven surfaces can also exacerbate these biomechanical issues - further increasing the risk of developing tendinopathy.
Genetic Tendencies
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to weaker tendons or connective tissues - making them more susceptible to injuries.
While you can't change your genetic makeup, being aware of this predisposition means that you can take proactive measures. Regular exercise, proper warm-ups, and listening to your body can help mitigate the risk. If you have a family history of tendon issues - consult a healthcare professional for personalised advice.
Treatment Options for Relief
Rest and Recovery Techniques
Initially, you must rest the affected area to allow the inflammation to subside. Avoid activities that exacerbate the pain, and apply ice packs to the groin area for 15-20 minutes several times a day. This helps reduce swelling and provides temporary pain relief.
During this period, gentle stretching and light activities that don't stress the adductors can be beneficial. Listen to your body and gradually reintroduce activities as the pain decreases.
Physical Therapy Interventions
A skilled therapist can design a personalised program to improve flexibility, strengthen the adductor muscles, and correct any biomechanical issues.
This program may include exercises to enhance hip stability, core strength, and balance. Techniques such as massage and ultrasound therapy can also aid in reducing muscle tension and promoting healing.
Medical Treatment Possibilities
In cases where pain persists despite conservative measures, medical interventions may be necessary. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
For more severe cases, a doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy to promote tendon healing. Surgery is rarely needed and is considered only when other treatments fail to provide relief.
Exercises for Recovery and Prevention
Stretching and Flexibility Routines
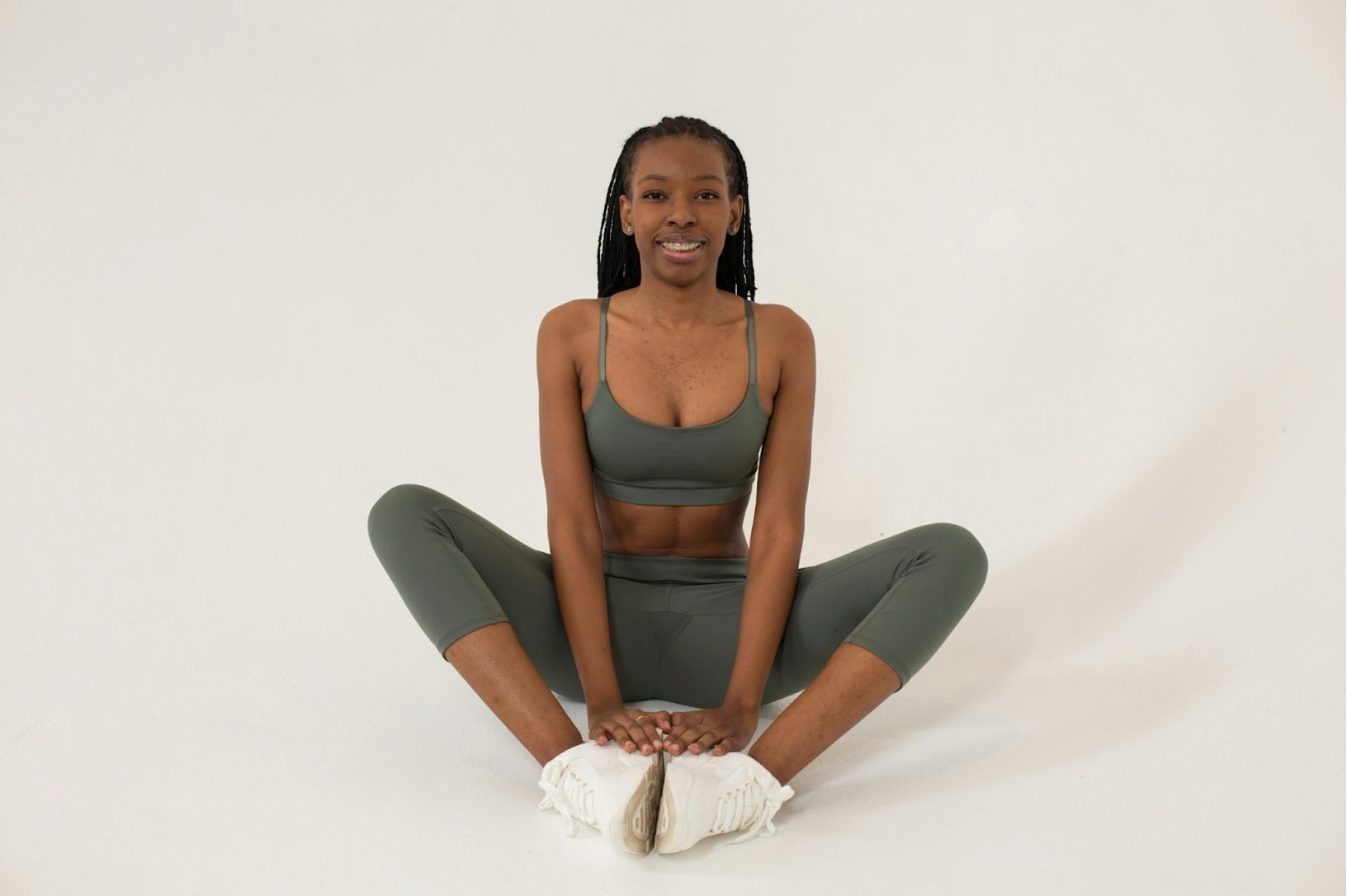

Stretching the adductor muscles is crucial for maintaining flexibility and preventing tightness.
Perform stretches like the butterfly stretch:
-
Sit with your feet together
-
And gently press your knees towards the floor.
-
Hold each stretch for 20-30 seconds
-
And repeat 3-4 times.
Strength-Building Exercises
Strengthening the adductor muscles and surrounding areas can provide better support and stability.
Include exercises like side lunges:
-
Step to the side
-
And bend your knee,
-
Keep the opposite leg straight.
-
Repeat 5 times
Another effective exercise is the adductor squeeze:
-
Lie on your back with your knees bent
-
Squeeze a ball between your knees.
-
Aim for 2-3 sets of 10-15 repetitions for each exercise.
Gradually increase the intensity and resistance as your strength improves to build resilience and prevent future injuries.
Sport-Specific Routines
For athletes, incorporating sport-specific routines is vital for addressing the unique demands of their sport. Soccer players, for instance, should focus on agility drills and lateral movements to mimic game scenarios.
Runners can benefit from plyometric exercises that enhance explosive power and stride efficiency. Customising exercises to your sport helps improve performance while reducing the risk of adductor tendinopathy.
Daily Habits for Healthy Tendons
-
Warm-Up: Always start with a proper warm-up before engaging in physical activities. This increases blood flow to the muscles and prepares them for exercise.
-
Stretching: Incorporate regular stretching routines to maintain flexibility and prevent muscle tightness.
-
Balanced Diet: Consume a diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support tendon health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish and nuts, are particularly beneficial.
-
Hydration: Stay well-hydrated to keep your muscles and tendons supple.
-
Rest: Allow adequate rest between workouts to give your tendons time to recover
Transforming Tendon Health at MSK Doctors
At MSK Doctors, we recognise that adductor tendinopathy is more than just a painful condition—it's a complex challenge that impacts your mobility, performance, and quality of life.
Our approach transcends traditional treatment, leveraging state-of-the-art musculoskeletal MAI-Motion AI technology to provide insights into your unique movement patterns and biomechanics.
We don't just treat symptoms; we decode the underlying causes of your tendon stress. Our team of leading orthopaedic consultants specialises in creating personalised treatment strategies that address your specific needs.

From advanced regenerative treatments to precision-guided rehabilitation, we offer a comprehensive approach that goes beyond conventional care.
Whether you're a professional athlete or an active individual, we provide sophisticated, targeted care that helps you return to peak performance.
Book your MSK Doctors adductor tendinopathy consultation today and let us help get back in control of your movement and health. Your journey to recovery starts now.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What exactly is adductor tendinopathy?
A condition characterised by damage and pain in the adductor tendons, typically caused by overuse or excessive strain during athletic activities.
Which sports are most likely to cause adductor tendinopathy?
Sports involving repetitive leg movements or sudden direction changes, such as soccer, hockey, basketball, and running.
Can adductor tendinopathy heal without surgery?
Most cases can be effectively managed through conservative treatments like rest, physical therapy, and targeted exercises.
How long does recovery typically take?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity, but most patients see improvement within weeks to months with proper treatment.
Why choose MSK Doctors for adductor tendinopathy treatment?
At MSK Doctors, we provide innovative, MAI-Motion AI-powered musculoskeletal care and specialised regenerative treatments, without any GP referral.
:format(webp)/cdn.mskdoctors.com/storage/2025/5/qf6zY2JVctL0BGJLEryU4lLIeRBsr5fC.jpg)
:format(webp)/cdn.mskdoctors.com/storage/2025/5/J26J2SuguZTzYNmqcI1EFk6a2wJsUF4a.jpg)
:format(webp)/cdn.mskdoctors.com/storage/2025/5/C4LMXVp2sVqlw6pSc34aXpbl7ZEFTXUS.jpg)
