Ischiofemoral Impingement Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Exercises
:format(webp)/cdn.mskdoctors.com/storage/2025/3/M8jCyrT8fPcmswfChuTe7GJ7hyMB5NS1.jpg)
Key Takeaways
-
Ischiofemoral impingement syndrome (IFI) causes pain due to narrowing between the ischium and femur.
-
Symptoms often include deep pain in the buttock and thigh, difficulty in movement, and muscle weakness.
-
Anatomical variations, age-related changes, and post-surgical complications can contribute to IFI.
-
Physical therapy, stretching exercises, and in some cases, surgery, are effective treatments.
-
MSK Doctors offers personalised treatment approaches, combining advanced diagnostic techniques with comprehensive rehabilitation strategies.
Understanding Ischiofemoral Impingement Syndrome
Ischiofemoral impingement syndrome (IFI) is a condition that affects the hip joint, causing pain and discomfort.
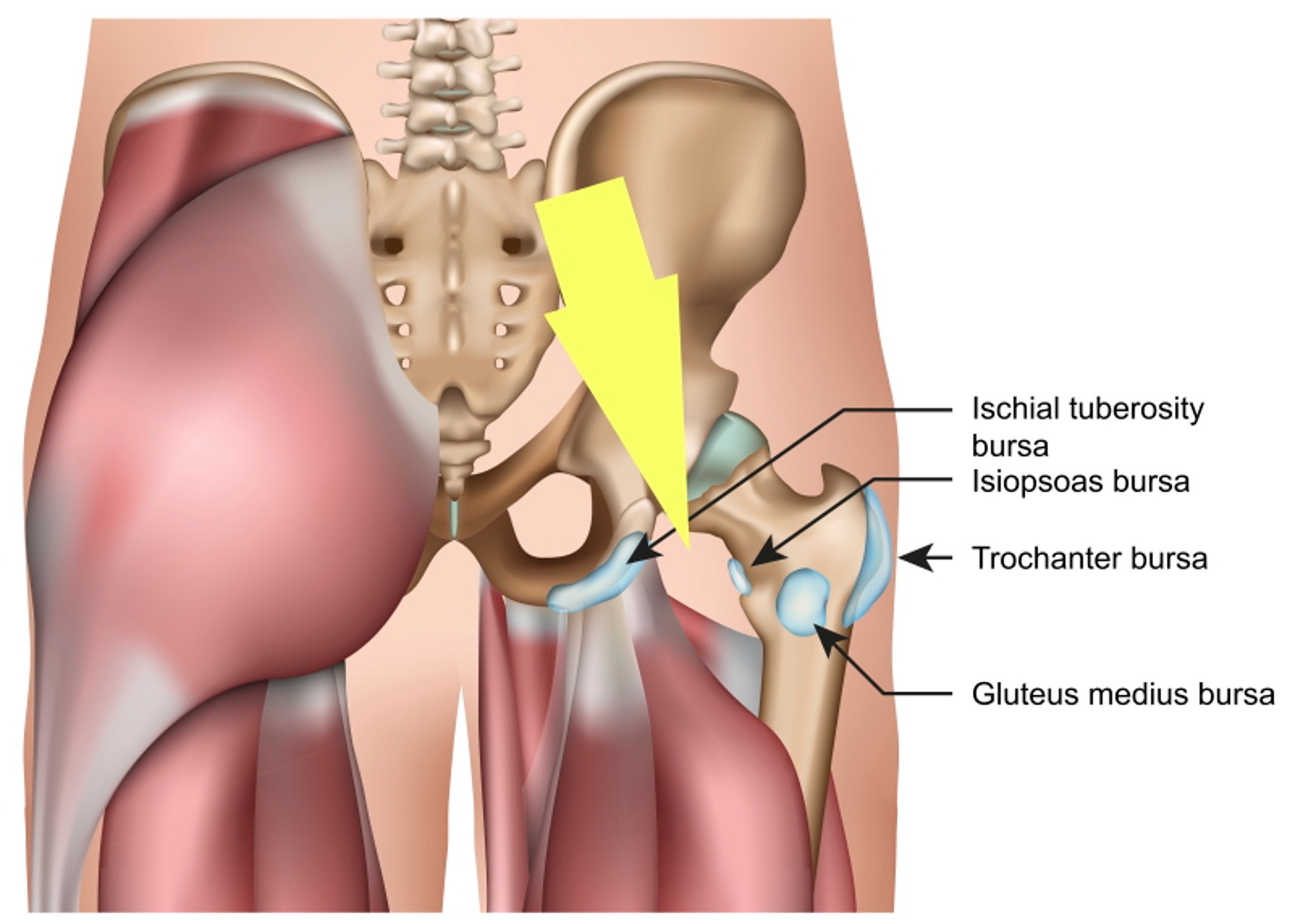
This syndrome arises when the space between the ischium, a part of the pelvis, and the femur, the thigh bone, becomes too narrow. This narrowing can lead to the compression of the quadratus femoris muscle and, in some cases, the sciatic nerve (image courtesy of Sport Doctor London).
Ischiofemoral impingement syndrome can affect anyone, but it is more commonly observed in middle-aged women. However, it can also occur in athletes or individuals who have undergone hip surgery.
|
Recognising Symptoms
Here are some of the common symptoms of IFI:
-
Pain in Buttock and Thigh: One of the most common symptoms of IFI is a deep, aching pain in the buttock and the back of the thigh. This pain often intensifies with physical activity, especially activities that involve hip extension or rotation.
-
Difficulty Moving: Individuals with IFI often experience difficulty in moving their hip joint freely. This can manifest as stiffness, a reduced range of motion, or a sensation of catching or locking in the hip.
-
Muscle Weakness: Muscle weakness, particularly in the affected leg, is another symptom of IFI.

Muscle weakness can make it challenging to perform daily activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, or even standing for extended periods.
Causes of Ischiofemoral Impingement
Anatomical Factors
Some individuals may have anatomical variations that predispose them to IFI. These variations can include a naturally narrow ischiofemoral space or changes in the shape of the femur or pelvis. Such structural differences can lead to the impingement of soft tissues in the hip.
Age-Related Changes
Degenerative changes, such as osteoarthritis, can lead to a narrowing of the ischiofemoral space. This narrowing can increase the likelihood of impingement, causing pain and discomfort in the hip area.
The natural wear and tear of cartilage and other soft tissues can exacerbate the problem too - making movement more difficult and painful.
Post-Surgical Complications
Individuals who have undergone hip surgery, such as total hip replacement or proximal femoral osteotomy, may experience ischiofemoral impingement as a complication.
Post-surgical changes in the alignment or positioning of the hip joint can alter the ischiofemoral space, leading to impingement.
Effective Treatments
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can design a personalised exercise program to help stretch and strengthen the muscles around the hip joint. This can improve flexibility, reduce pain, and prevent further impingement.
Regular therapy sessions can also teach individuals how to modify their movements to avoid aggravating the condition.
Medication Options
In some cases, medications may be necessary to manage the pain and inflammation associated with IFI. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can be effective in reducing swelling and discomfort.
However, use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid potential side effects and interactions with other treatments.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical options can include procedures to widen the ischiofemoral space or to remove any bony abnormalities contributing to the impingement. While surgery can provide significant relief, it is typically viewed as a last resort after other treatments have been exhausted.
Rehabilitation Exercises
Stretching Techniques
Gentle stretches can help increase the range of motion in the hip joint and reduce muscle tension and pain associated with IFI. Here are some effective stretching techniques:
-
Hip Flexor Stretch: Kneel on one knee with the other foot in front, forming a 90-degree angle. Push your hips forward gently while keeping your back straight. Hold for 20-30 seconds.
-
Piriformis Stretch: Lie on your back with your knees bent. Cross one ankle over the opposite knee and gently pull the uncrossed leg towards your chest. Hold for 20-30 seconds.
Strengthening Routines
Strengthening the muscles around the hip joint can provide support and stability, reducing the risk of impingement. Focus on exercises that target the glutes, quadriceps, and core muscles:
-
Leg Raises: Lie on your side with legs straight. Lift the top leg towards the ceiling, keeping it straight, and then lower it back down slowly.
-
Glute Bridges: Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Lift your hips towards the ceiling, squeezing your glutes at the top. Hold for a few seconds before lowering.
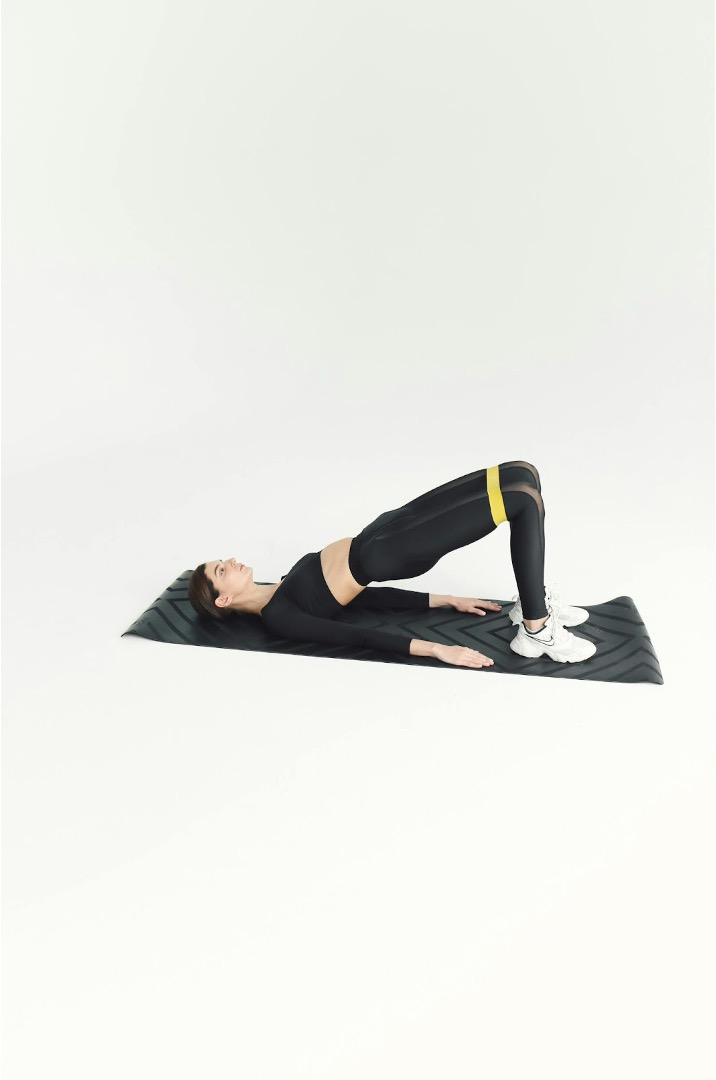

Incorporate these exercises into your routine to build strength and support for your hip joint. The image above shows glute bridge exercise.
Balance and Stability
Improving balance and stability can further protect the hip joint from impingement. These exercises challenge your balance and can improve your proprioception and coordination:
-
Single-Leg Stance: Stand on one leg, holding the position for 30 seconds. Switch legs and repeat. For an added challenge, try closing your eyes.
-
Balance Board Exercises: Use a balance board to perform gentle rocking motions. This can help improve stability and strengthen the muscles around the hip.
Achieving Long-Term Mobility
Long-term management of ischiofemoral impingement syndrome involves regular follow-ups with healthcare providers and adherence to prescribed exercise routines.
Continue practicing stretching and strengthening exercises even after symptoms improve, as this helps maintain joint health and prevent future issues.
Your Path to Recovery with MSK Doctors
At MSK Doctors, we don't just treat your condition; we empower you with comprehensive care.
Our approach integrates advanced diagnosis methods like MAI-Motion, cutting-edge rehabilitation techniques, and a deep commitment to your individual healing journey.

From initial assessment to targeted therapeutic interventions, we ensure you receive expert, compassionate care suited specifically to your unique physiological needs.
Contact MSK Doctors today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a pain-free life today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How quickly can IFI symptoms develop?
Symptom progression varies, but patients often report gradual onset with increasing intensity over weeks to months, depending on underlying pathological mechanisms.
Can IFI be prevented?
While not entirely preventable, maintaining muscular flexibility, balanced strength training, and addressing anatomical predispositions can reduce potential impingement risks.
Are there long-term complications if left untreated?
Unmanaged IFI may lead to chronic pain, muscular atrophy, reduced joint mobility, and potential nerve compression, underscoring the importance of early intervention.
Is surgery always necessary for IFI treatment?
Surgical intervention is typically a last resort. Most cases respond effectively to conservative treatments like physiotherapy, targeted exercises, and pain management strategies.
What distinguishes MSK Doctors in treating IFI?
At MSK Doctors, our specialist team offers evidence-based treatment protocols, integrating advanced diagnostic techniques with comprehensive rehabilitation strategies tailored to individual patient needs.
:format(webp)/cdn.mskdoctors.com/storage/2025/5/kYXD4QhVns5eRrVtORrPUcpF5e27nSoi.jpg)
:format(webp)/cdn.mskdoctors.com/storage/2025/5/rjqVktimIUo4bjk754izhQm3rJFiCYTG.jpg)
:format(webp)/cdn.mskdoctors.com/storage/2025/5/MlcNonCFo5OxhqZcRB2DwwINYJlpWDcB.jpg)
