Understanding ACL Tear: Symptoms, Causes, and Recovery
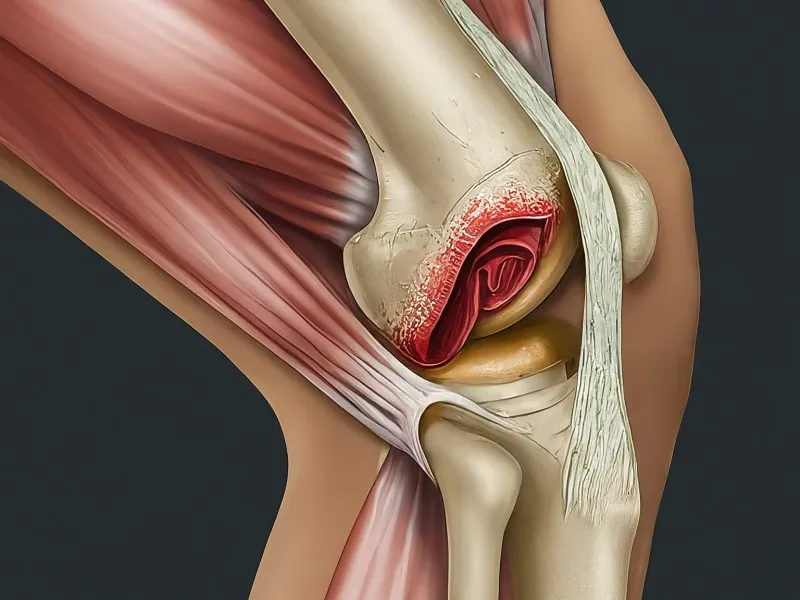
An ACL tear, or anterior cruciate ligament tear, is a common knee injury, especially among athletes. The anterior cruciate ligament is crucial for stabilising the knee during various activities. Common causes include sudden stops, jumps, or direction changes during sports like football, basketball, and skiing. Patients who have sustained an ACL injury often describe hearing a popping sound at the moment of the tear. Initial symptoms typically include severe pain, rapid swelling, a feeling of instability, and difficulty walking.
Understanding an ACL Tear
The ACL is one of the four main ligaments in the knee and connects the thigh bone to the shin bone. It is crucial for maintaining knee stability. An ACL tear can range from a mild sprain to a complete rupture. Diagnosis typically begins with a physical examination and may be confirmed with imaging tests such as MRI. Common indicators include the Lachman test and the pivot shift test. Diagnosis of an ACL tear is crucial for opting for the right treatment plan—whether it’s surgical or non-surgical.
Impact and Associated Injuries
A torn ACL can severely impact a person’s mobility and quality of life. The immediate effect is usually marked by discomfort and restricted movement. Untreated ACL tears can lead to further injuries, such as meniscal tears and damage to other ligaments like the posterior cruciate ligament. Over time, the condition can lead to chronic instability and even osteoarthritis. Addressing an ACL tear promptly is vital to prevent more severe complications.
Side Effects and Complications of ACL Tears
Short-term side effects of an ACL tear include pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion. Long-term effects can involve chronic knee pain, prolonged instability, and an increased risk of osteoarthritis. If left untreated, complications may include frequent knee giving way, further cartilage damage, and an array of secondary injuries. Effective management is critical to avoid these progressive complications and to ensure a functional recovery.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
The recovery process for an ACL injury typically spans several months. Post-surgery, initial recovery focuses on controlling pain and swelling, regaining range of motion, and starting light strengthening exercises. Rehabilitation plays a pivotal role, typically divided into three phases:
- Initial Stage (0-6 weeks): Emphasis on reducing swelling and achieving a full range of motion.
- Intermediate Stage (7-12 weeks): Focus on building strength and improving knee stability through targeted exercises.
- Advanced Stage (3-6 months): Introduction of sport-specific drills and high-intensity exercises to prepare for return to activity.
Barriers to recovery can include lack of adherence to the rehabilitation programme, secondary injuries, and insufficient muscle strength. To overcome these, it’s essential to follow a structured rehab plan under the supervision of healthcare professionals.
Additional Patient Information
Early intervention is crucial for a positive outcome in ACL injuries. Preventive measures include strengthening the surrounding muscles, practising proper techniques during sports, and using appropriate gear like knee braces. Immediate medical advice should be sought in cases of severe pain, persistent swelling, or recurrent instability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What should I do immediately after an ACL tear?
Apply ice to reduce swelling, keep the joint elevated, and avoid putting weight on the leg. Seek immediate medical attention for a proper diagnosis. - How long does it take to recover from an ACL injury?
Recovery time varies but generally takes about 6-9 months depending on the severity of the tear and the patient’s adherence to the rehabilitation programme. - Can I prevent future occurrences of an ACL tear?
Strengthening leg muscles, improving flexibility, and practising proper techniques during sports can help prevent future ACL injuries. - What are the signs of complications after an ACL injury?
Signs of complications include persistent swelling, severe knee instability, and chronic pain. Consult a healthcare provider if these symptoms persist. - How effective is physical therapy for recovery from an ACL injury?
Physical therapy is highly effective and critical for regaining knee strength, stability, and range of motion, which are essential for a successful recovery. - When should I consider surgery for an ACL tear?
Surgery is usually considered if conservative treatments fail, if there is significant instability, or if the individual is keen on returning to high-demand sports.
Remember, ACL injuries require timely medical intervention and a dedicated rehabilitation programme for optimal recovery. Always consult with healthcare professionals to tailor a recovery plan suited to your specific needs.
